Insurance Planning
take look at our
Risk Analysis & Insurance Planning








What is Risk analysis and Insurance planning?
Risk analysis and Insurance planning services incorporates analysing the risk profile and insurance coverage required for the individual relating to its health, life and vehicles.
We analyse:-
1. the risk appetite of the individual regarding to its heath, life and vehicle based on the various factors considered by us etc.
2. Amount of insurance cover required by the individual.
3. Advising and providing the apt insurance policy on the basis of the factors analysed by us for the clients.
4. Providing the reports of the premiums, sum assured, charges etc for the policy taken.
Insurance Planning
Insurance is a form of risk management primarily used to hedge against the risk of a contingent, uncertain loss. Insurance is defined as the equitable transfer of a loss, from one entity to another, in exchange for payment. INSURANCE PLANNING is the process of identifying the potential sources-of financial risk for an individual client and his/her family and securing the client against the same by using different risk management techniques, including buying of insurance policies. Everyone who wants to protects themselves or someone else against financial hardship, should consider insurance. This may include:
- Protecting family after one’s death from loss of income
- Ensuring debt repayment after death
- Covering contingent liabilities
- Protecting against the death of a key employee or person in your business
- Buying out a partner or co-shareholder after his or her death
- Protecting your business from business interruption and loss of income
- Protecting yourself against unforeseeable health expenses
- Protecting your home against theft, fire, flood and other hazards
- Protecting yourself against lawsuits
- Protecting yourself in the event of disability
- Protecting your car against theft or losses incurred because of accidents And many more.

Importance of Insurance
These questions help an investor as well as a wealth manager to understand where , when and what to invest. In establishing goals and objectives for the use and transfer of wealth, you probably prioritize them in this order: self and spouse, heirs (children and grandchildren), and community needs and opportunities. It is important to develop a wealth management plan that matches your priorities. Lifestyle maintenance your most important planning objective is to maintain your current lifestyle and ensure your financial independence. One of the major obstacles to effective planning is the gap between the perception of wealth and reality of wealth. Thus, you should clearly define what is required to maintain your current lifestyle. In other words, the annual income needed for personal consumption and material assets (house, car, vacation home) to maintain your lifestyle and adequate liquidity. Wealth transfer to heirs most likely, you want your heirs to be safe and comfortable, to help them become established and successful in life, and to provide for their medical or housing needs if they meet unexpected emergencies. In addition, you want your children and grandchildren to exhibit character, mental strength, integrity, a sense of family legacy, and responsible behaviour– attributes money can’t “buy.” In short, you want your heirs to be self-supporting, but would like to provide both selected advantages and a “safety net.” Only you can decide how much is enough to leave your heirs. Many couples discover that if they do nothing, they will leave their children much more than they really believe is necessary or appropriate. Defining an appropriate specific inheritance requires careful consideration of each individual heir. What is appropriate for one is not necessarily appropriate for another. Your job is to identify specific assets or lifestyle attributes you would like your heirs to enjoy as a result of receiving an inheritance.
Our Role in Wealth Management
- reduce worry and fear
- invisible earnings
- social benefits
- make available funds for investment
- enhance credit worthiness
Risk Management
Risk management is about recognizing what these uncertain events are, how severe they may be and how they can be controlled. Risk management involves “The identification, analysis and economic control of those risks which can threaten the life, assets or earning capacity of an individual/enterprise.
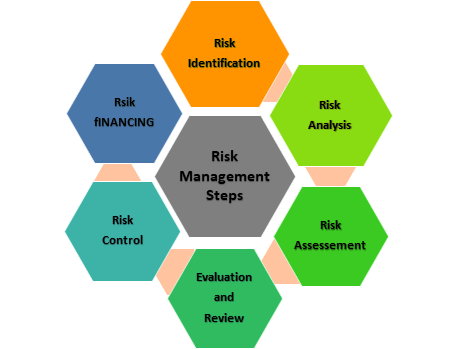
Steps in Risk Management
The cost of risk can be looked at from a number of different perspectives. There is at least the: (a) Frequency of risk; (b) Monetary cost or financial severity; (c) Human cost in terms of pairs and suffering. The risk manager evaluates the risks that are identified. This means that measuring the potential size of the loss and the probability that it is likely to occur. Critical risks include all exposures in which the possible losses are of a magnitude that would result in bankruptcy. Important risks include those exposures in which the possible losses would not lead to bankruptcy, but would require the firm to borrow in order to continue operations. Unimportant risks include exposures in which the possible losses could be met out of the existing assets or current income of the firm without imposing undue financial strain.
People are concerned with the manner in which those risks that remain after the risk control measures have been implemented, shall be financed. It has to be recognized that in the long run an individual/organization will have to pay for its own losses. Therefore the primary objective of risk financing is to spread more evenly over time, the cost of risks in order to reduce the financial strain and possible insolvency, which the random occurrence of large losses may cause. The secondary objective is to minimize the cost of risk. An individual or organisation can finance its risk costs in the following manner: • Payment out of current expenses • Through a funded or non-funded reserve • By debt or equity financing • By pre or post credit • By forming a captive, a trust, by pooling, or through a spread-loss plan. The probability and severity of possible losses play an important part in the structing of a risk-financing programme.
Risk Management

Health Insurance
Health insurance in India is a growing segment of India's economy. The Indian health system is one of the largest in the world, with the number of...read more.
Life Insurance
Buying life insurance is one of the most important financial decisions, but believe it or not, only 10 per cent of Indians are insured. But why it so important? Well, regardless...read more.

General Insurance
General Insurance helps us to protect ourselves and the things we value, such as our homes, our cars and our valuables, from the financial uncertainties like...read more.
What Mudraguna Provides Through Risk Analysis & Insurance Planning
RISK ANALYSIS & INSURANCE PLANNING SERVICES
Risk analysis and Insurance planning services incorporates analysing the risk profile and insurance coverage required for the individual relating to its health, life and vehicles.
- We analyse the risk appetite of the individual regarding to its heath, life and vehicle based on the various factors considered by us etc.
- Amount of insurance cover required by the individual.
- Advising and providing the apt insurance policy on the basis of the factors analysed by us for the clients.
- Providing the reports of the premiums, sum assured, charges etc for the policy taken.
YOUR ROLE IN RISK ANALYSIS & INSURANCE PLANNING
In insurance there is a contract between two parties insurer and insured where the principle of “Caveat Emptor” does not apply as the contract is based on the revealing of many facts which –
- Are known only to the proposer, and
- Insurer cannot know them, if the proposer does not disclose them.
These facts relate to the individual’s health, habits, personal history, family history, etc. The insurer (person providing the policy) cannot possibly be aware of all these details unless the proposer discloses them.
Non-disclosure of these facts may adversely affect the interest of the insurer and thereby the community of policy holders. Hence, disclosure of the material facts (Material facts means “Every circumstance is material which would influence the judgment of a prudent insurer in arriving at the decision to accept risk and fix premiums.” Therefore, facts regarding age, height, weight, build, previous medical history, smoking/drinking habits, operations, diseases suffered, non-disclosure of earlier insurances, hazardous occupation must be disclosed.) by the clients is must which helps the insurer in providing the apt insurance policy.
Hence, it is the duty of the client to provide the right and correct information which has been asked from him which will help the insurer to provide the right and suitable insurance policy as per the requirement of the client.
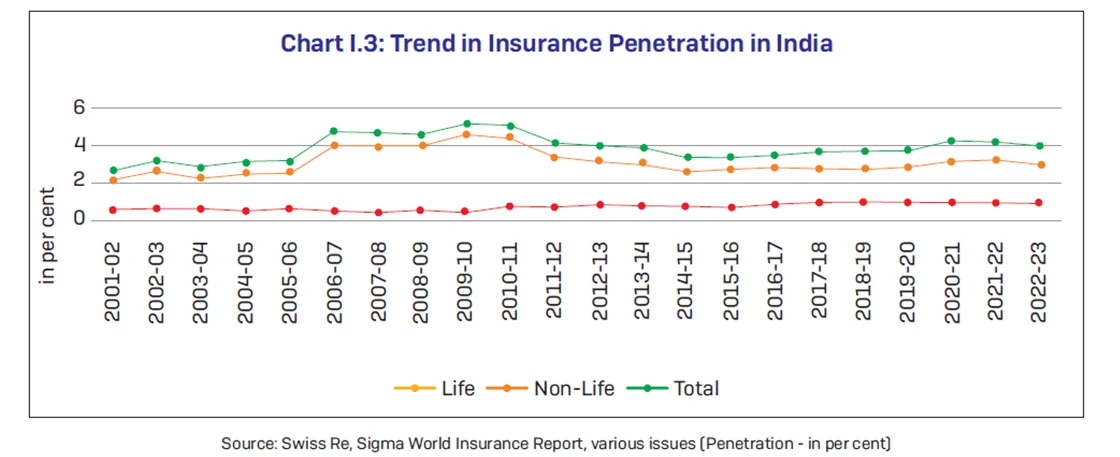
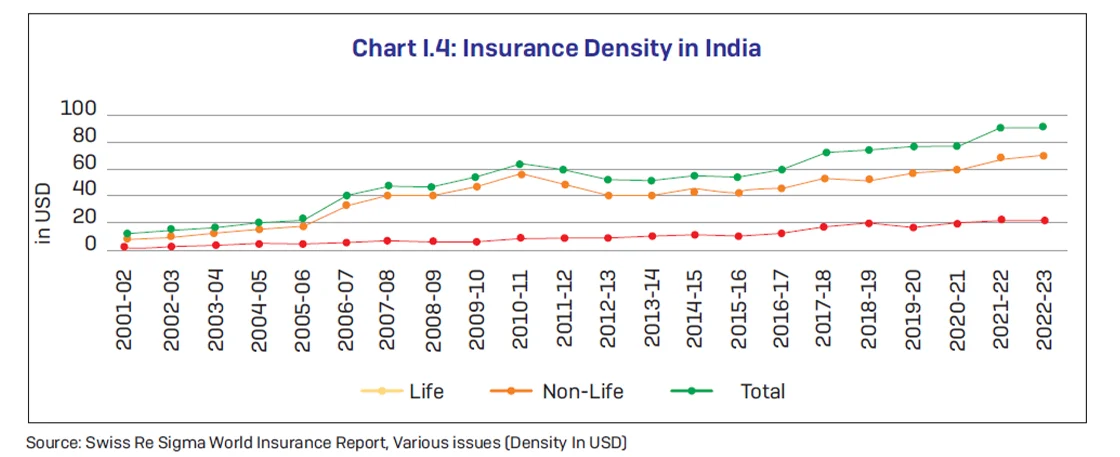
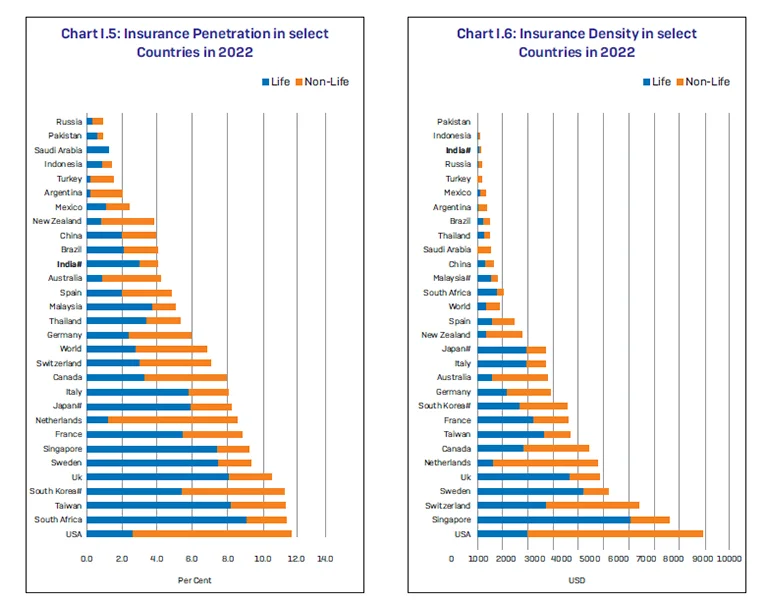
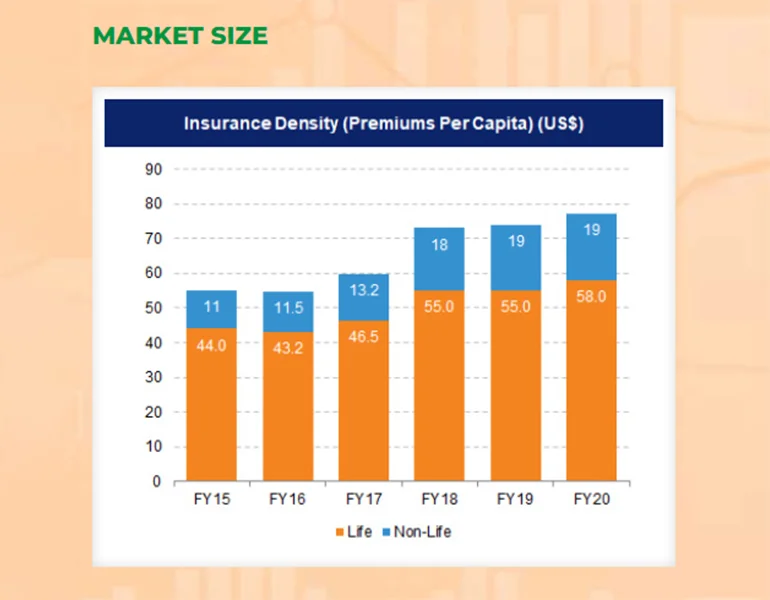
Insurance Industry Market Trends